Continental
Autonomous Quality in PCB Production for Future Mobility

Continental AG is a German based global Automotive Supplier. Main areas of activity are Safety and Motion, Architecture and Network, Smart Mobility, User Experience, Autonomous Mobility, Conti Tech and Rubber Products.
In 2021 Continental did 33,8 Billion sales supported by 190000 Employees in 527 sites in 58 countries.
Process Challenges
The automobile of the future will have increasingly self-driving features next to the electrification of road transport. In consequence this development triggers a strong shift towards highly reliable and often new electronic components and systems in the motor cars to come.
Volatile global markets with varying customer preferences and the demand for strict cost control set the corner stones, which are:
- achievement of highest product and system quality for very large lot sizes
- keeping close cost control in line with the OEMs cost ceilings
- remaining highly reactive regarding time-to-market, as well as volume-to-market For a PCB production site with an average manufacturing capacity of 30 to 40 million pcs per year quality, availability and efficiency are crucial.
Process Value
The production of automotive electronics for future mobility is based on automated lines that secure highest quality and output. For the production and assembly of respective PCBs an effective zero-defect approach and availability is paramount.
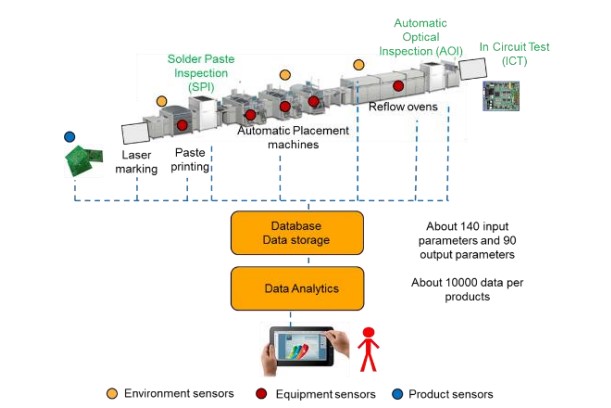
A single SMD line is used to assemble PCBs and Electronic components and follows a generic design. SMD line production consists of 4 different operations: Laser marking, paste printing, placement, reflow oven and three different inspections: Solder Paste Inspection, Automatic optical inspection, and In-circuit testing.
As shown in Fig. numerous sensors in combination with advanced data processing allows the control and operation of a single line with three operators, only. “Autonomus Quality” for a 1st Tier Automotive supplier is defined by:
- a single electronic PCB product regarding current and future mobility demands,
- an interactive SMD line
- the full production site.
Experiment Performance
ATB – SINTEF Contribution – Big Industrial Data Analytics and online Data Aquisition
- Identification of PCB customer returns as outliers using Sintef’s Principal Component Analysis and Mahalanobis Distance algorithms
- Filtering of Critical to Quality variables using domain expertise via the quality team at Sibiu, Romania
- Cooperation with ATB Bremen to create an operational automated solution for dataset extraction, preprocessing and formatting, analysis and results output to a graphical user interface inside Continental’s network
- Fully «white box» general solution sensitive to format, but not unit type, unique units or number of variables
Continental and Fraunhofer IAO collaborate on semantic search technology Introduction
- Continental team members at analysis stations have the permanent challenge to record failures in short time and match identified failures to a standard failure catalogue and past time failures.
- Fraunhofer IAO Semantic Search technology enables Search for corresponding Defect Name with user input based on a Defect Catalogue
PACE WEAVR supports reduction of human effort on the shopfloor
- Continental team members permanently have to do Training, Maintenance and Repair
- PACE provides technology using augmented reality for virtual assistance for these tasks
- Team members are freed up as the virtual assistance can take over routine tasks in Training, Maintenance and Repair
TUBS contribution
Problem Statement:
- Integration of new product variants leads to frequent pseudo errors, as “optimal” control limits (upper and lower) are unknown.
- Measuring needles of the ICT are wearing out and lead to failure and downtime of the inspection system.
Solution Approach:
- Development of a methodology for data-based analysis and modeling of the abrasion of individual measuring needles.
- With help of a visualization, the analysis and modeling results are made accessible to the user:
- Identification and presentation of trend analysis with regard to ICT measuring points towards upper or lower limits
- Visualization of the specific measuring needle on the adapter for quick identification and replacement
Value chain
Observations & Lessons learnt
BP1: Effort for Training was reduced significantly.
Trainers have more time now for Operational and Tactical activity on the shopfloor. Training can happen virtually to a large extent.
Through Change over and Maintenance there is less discussion and corrective action necessary. Preparation time for these activities went down to almost zero.
BP2: The possibility of early detection of defective parts by using statistical data analytics is proven! KPI PPM rate has a potential of 20% Reduction
BP3: Bad defect description can be avoided and high efforts for defect description are reduced by the technology. Response time for searches in the failure database is impressively low.
BP4: In the ICT area as well pseudo failures reduction and less time for Analyses can be observed.
Replication Potential
BP1: As this activity is executed as a pilot, Continental is planning to make use of the Technology to a larger extent in the future.
BP2: Continuation of cooperation is planned with or without funding.
BP3: Collaboration model needs to be further discussed.
BP4: Visual aids potential will be investigated in other areas in the future
Logistics Automotive Manager 2008 – 2012
Electronics Plants Manager 2012 – 2014
Plant Manger 2014 – 2016
IT Manager Manufacturing Applications since 2016
Continental | Sibiu, Romania
Pilot Partners
Standards used
- MQTT
- OPCUA
- Kubernetes
- Docker
Big Data Platforms & Tools
- AWS
- Continental Manufacturing Data Lake
- Git Hub
Big Data Characterization
Data types
- Product characteristics
- Outliers
Number of sources
- Multiple Test stations
- Analytics stations
Open data
No
Key Facts & KPIs
Productivity
OEE – Overall Equipment Efficiency
FPY – First Pass Yield
Speed
MTTR – Mean time to repair
Time to analyse NOK tested Products
Sustainability
Scrap reduction
Agility
Time for Training of Production staff
Adoption Assessment
![]()
![]()
![]()
Technical feasibility
![]()
![]()
![]()
Economic feasibility
![]()
![]()
![]()
Replication potential